As a key state in the nation’s cultural and economic fabric, Iowa’s significance extends beyond its borders.
Iowa is often symbolized by its rich agricultural heritage, earning it the nickname “Food Capital of the World.”
In addition to its agricultural prowess, Iowa harbors diverse landscapes, ranging from the Loess Hills in the west to the Driftless Area in the northeast. These geographical features add to the state’s scenic beauty, offering numerous outdoor recreational opportunities.
Quick facts
Iowa by the Numbers
3,190,369
Population (2022)
1846
Year of Statehood
56,273
Area (Square Miles)
Map of Iowa
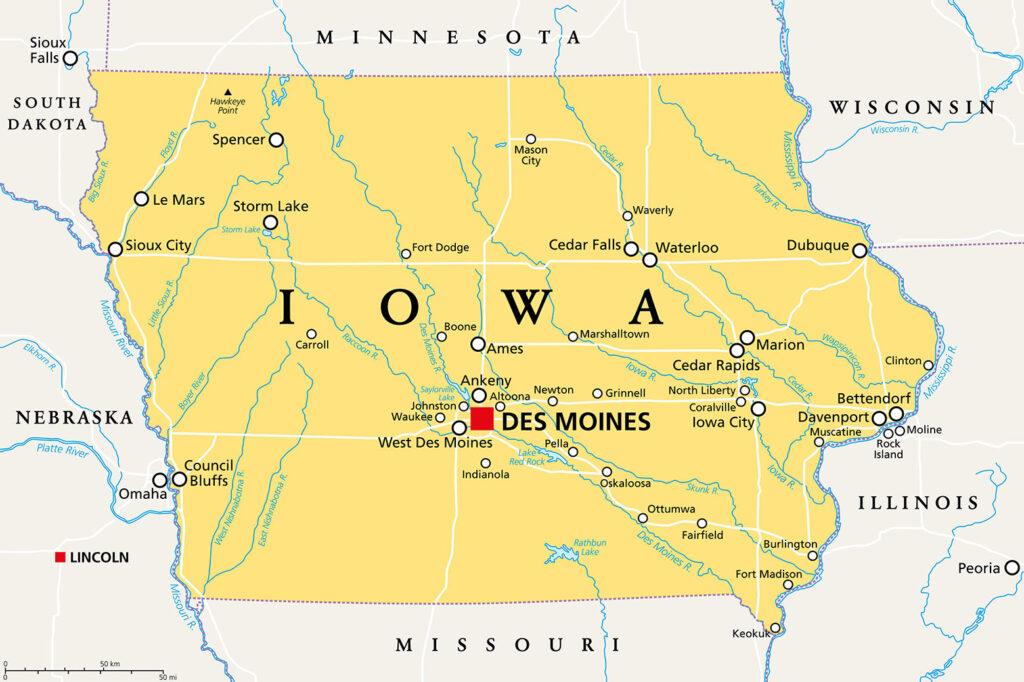
Iowa, often referred to as the Hawkeye State, presents a unique demographic landscape reflective of its diverse cultural and social fabric.
A Brief History of Iowa
Iowa’s Unique Climate and Geography
The Economy of Iowa
Known for its robust agricultural sector, Iowa’s economy is deeply rooted in farming, making it a key player in the United States’ agricultural production. As a leading producer of corn, soybeans, and pork, Iowa significantly contributes to the nation’s food supply. The state harnesses its fertile soil and favorable climate to cultivate vast expanses of corn and soybeans, underpinning local and national markets. Pork production is equally significant, with Iowa ranking consistently at the top for its hog farming, benefiting from the integration of advanced farming techniques and efficient supply chains.
Beyond agriculture, Iowa has diversified its economic landscape through strong manufacturing and renewable energy sectors. The manufacturing industry, while historically linked to agricultural machinery, has expanded into producing a variety of goods, from food products and chemicals to machinery and equipment. This diversification has allowed the state to maintain economic balance and resilience. Renewable energy, notably wind power, has seen substantial growth, positioning Iowa as a leader in green energy production. Wind turbines dot the landscape, harnessing the state’s natural breezes to provide clean energy and create numerous jobs within the sector.
Employment in Iowa reflects these diverse economic activities. Agriculture remains a significant employer, but manufacturing also provides substantial job opportunities. The renewable energy sector has emerged as a vital source of employment, requiring skilled labor and contributing to workforce growth. As of the latest reports, Iowa enjoys a relatively low unemployment rate, attributed to its well-rounded economy and proactive job creation efforts. However, the state faces challenges such as the need for continued investment in workforce development, especially to meet the evolving demands of advanced manufacturing and green energy. Additionally, fluctuations in commodity prices and international trade dynamics pose risks to the agricultural sector.
While economic challenges persist, Iowa’s successes are evident in its ability to adapt and sustain growth across multiple industries. Through strategic investments and continued innovation, the state is poised to strengthen its economic foundation further, ensuring long-term prosperity for its citizens and maintaining its vital role in the broader American economy.
Education and Institutions in Iowa
Iowa’s educational landscape exemplifies a strong commitment to quality and accessible education. The primary and secondary education systems in the state are well-regarded for their comprehensive curricula and excellent student outcomes. Iowa consistently ranks among the top states in reading and math proficiency, thanks in part to its dedicated educators and well-structured educational policies. School districts across the state benefit from funding that supports both academic and extracurricular activities, ensuring a balanced and enriching experience for students.
Higher education in Iowa is notably robust, anchored by two major public universities: the University of Iowa and Iowa State University. The University of Iowa, located in Iowa City, is renowned for its research contributions, particularly in the fields of medicine and the humanities. Its College of Medicine and Writers’ Workshop are both highly esteemed, contributing to Iowa’s reputation as a center of learning and innovation. Meanwhile, Iowa State University, situated in Ames, is distinguished for its focus on science, technology, engineering, and agriculture. Its research facilities and extension programs play a crucial role in advancing agricultural practices and sustainability efforts, impacting not just the state but also the national and global community.
Beyond these flagship institutions, Iowa is home to many other reputable colleges and universities, including private colleges that contribute to the state’s diverse educational environment. Institutions like Drake University and Grinnell College provide high-quality liberal arts education and foster critical thinking and leadership skills.
The state has also initiated several programs to improve education, targeting various aspects from early childhood education to higher education reforms. For instance, the Iowa STEM initiative aims to enhance students’ interest and performance in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics through innovative teaching and learning opportunities. These initiatives are designed to ensure that Iowa remains at the forefront of educational excellence, preparing students for the demands of the modern workforce and beyond.
